Embarking on a journey towards a healthier lifestyle can be overwhelming, particularly when faced with a myriad of dietary trends and conflicting information. This comprehensive nutrition coaching guide aims to provide clear, research-backed advice to help you make informed choices about your diet, exercise and overall well-being. We’ll cover balanced meal planning, food label interpretation, healthy dining out choices, dietary restrictions, macro and micronutrients, daily calorie needs, hydration, exercise and various dietary approaches, such as Keto, Paleo and Vegan.
Table of Contents for Nutrition coaching:
Balanced Meal Planning:
1.1. Macronutrients 1.2. Micronutrients 1.3. Meal Planning Strategies 1.4. Meal Plan Examples
2. Food Label Interpretation:
2.1. Understanding Food Labels 2.2. Serving Sizes 2.3. Nutritional Information
3. Healthy Dining Out Choices:
3.1. Tips for Dining Out 3.2. Cuisine-Specific Recommendations
4. Dietary Restrictions:
4.1. Vegetarian and Vegan 4.2. Gluten-Free 4.3. Lactose Intolerance 4.4. Food Allergies
5. Daily Calorie Needs:
5.1. Calculating Your Calorie Needs 5.2. Adjusting Calories for Weight Goals
6. Hydration:
6.1. Importance of Hydration 6.2. How Much Water to Drink Daily 6.3. Hydration Tips
7. Exercise and Nutrition:
7.1. Exercise Types 7.2. Nutritional Considerations for Different Exercises 7.3. Exercise Routines for Various Fitness Levels
8. Dietary Approaches and Trends
8.1. Keto 8.2. Paleo 8.3. Vegan 8.4. Pros and Cons of Each Approach
9. Research-Backed Evidence
9.1. Reliable Sources for Nutrition Information 9.2. Debunking Common Myths
10. The Role of a Nutrition Coach
10.1. Personalised Guidance and Support, 10.2. Accountability and Goal Setting, 10.3. Education and Skill Building 10.4. Ongoing Support and Adaptation
10. Conclusion
Balanced Meal Planning

1.1. Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the main components of our diet, which are essential for providing energy and supporting various bodily functions. They include carbohydrates, proteins and fats. To achieve a balanced diet, it’s crucial to consume the right balance of these macronutrients. A nutrition coach can help you understand the appropriate ratio for your individual needs.
1.2. Micronutrients
Micronutrients are the vitamins and minerals necessary for maintaining good health. They play vital roles in various physiological processes and are required in small amounts. Consuming a diverse, nutrient-dense diet is essential for getting adequate micronutrients. A nutrition coach can guide you in selecting the right foods to ensure sufficient micronutrient intake.
1.3. Meal Planning Strategies
- Assess your individual needs: Consider factors such as age, weight, activity level and health goals to determine your dietary needs. A nutrition coach can help you tailor your meal plan to your specific requirements.
- Portion control: Use measuring cups, scales or visual cues to manage portion sizes. • Create a weekly meal plan: Outline your meals and snacks for the week to stay organised and avoid unhealthy choices.
- Prioritise whole foods: Focus on consuming whole, minimally processed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats.
- Plan for variety: Include a wide range of foods to ensure you’re getting all essential nutrients. A nutrition coach can provide guidance on incorporating a diverse array of foods into your meal plan.
1.4. Meal Plan Examples
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with berries, chia seeds and Greek yoghurt
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, avocado and a light vinaigrette
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa • Snack: Carrot sticks with hummus or a handful of mixed nuts
Food Label Interpretation

2.1. Understanding Food Labels
Food labels provide essential information about the nutritional content of a product. Learning how to interpret them can help you make healthier choices and avoid hidden sugars, fats and additives. A nutrition coach can help you become proficient at reading food labels.
2.2. Serving Sizes
Check the serving size listed on the label, as it may differ from what you consider a standard portion. Nutritional information is based on this serving size, so be mindful of how much you’re consuming. Your nutrition coach can provide guidance on appropriate serving sizes.
2.3. Nutritional Information
Pay attention to key nutrients such as calories, fats (saturated and trans), carbohydrates (including sugars and fibre), protein and sodium. Choose products with lower levels of saturated fat, sugar and sodium and opt for those with higher amounts of fibre and protein. A nutrition coach can help you understand which nutrients to focus on based on your health goals.
Healthy Dining Out Choices
3.1. Tips for Dining Out
- Research the menu: Review the menu ahead of time to identify healthier options. Your nutrition coach can provide advice on making healthier choices when dining out.
- Watch portion sizes: Share an entrée, ask for a smaller portion or take leftovers home.
- Customise your meal: Request substitutions or modifications to make dishes healthier, such as asking for sauces or dressings on the side.
- Be mindful of beverages: Opt for water, unsweetened tea or a small glass of wine instead of sugary drinks.
3.2. Cuisine-Specific Recommendations
- Italian: Opt for tomato-based sauces instead of cream-based and choose grilled or steamed dishes over fried ones.
- Mexican: Choose soft corn tortillas over flour tortillas and avoid dishes with heavy cheese or sour cream.
- Asian: Opt for steamed or stir-fried dishes and request brown rice instead of white rice. A nutrition coach can offer additional guidance on navigating specific cuisines.
Dietary Restrictions
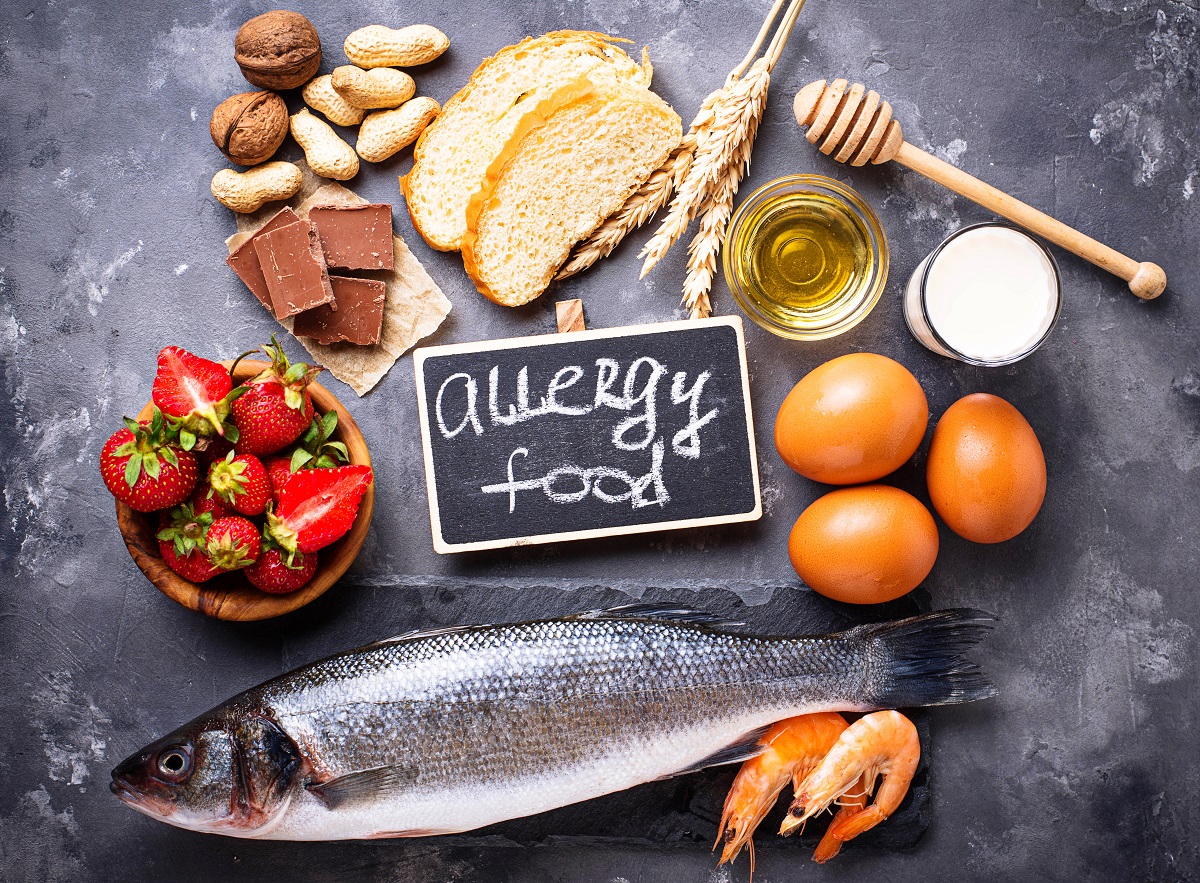

4.1. Vegetarian and Vegan
- Ensure adequate protein intake through plant-based sources like legumes, tofu, tempeh and whole grains.
- Include fortified foods or supplements for nutrients like vitamin B12, iron and omega-3 fatty acids. A nutrition coach can help tailor your vegetarian or vegan diet to meet your nutritional needs.
4.2. Gluten-Free
- Replace wheat-based products with gluten-free alternatives like rice, quinoa and gluten-free oats.
- Be mindful of cross-contamination and hidden sources of gluten in processed foods. A nutrition coach can provide guidance on following a gluten-free diet safely and effectively.
4.3. Lactose Intolerance
- Choose lactose-free dairy products or non-dairy alternatives like almond, soy or oat milk. A nutrition coach can help you identify suitable substitutes for dairy products.
4.4. Food Allergies
- Carefully read food labels for allergen information.
- Inform restaurant staff of your allergies when dining out to ensure safe food preparation.
- Carry an epinephrine auto-injector if prescribed by your healthcare provider. A nutrition coach can provide support in managing food allergies and creating a balanced diet while avoiding allergens.
Daily Calorie Needs

5.1. Calculating Your Calorie Needs
To calculate your daily calorie needs, consider factors such as age, sex, weight, height and activity level. Use online calculators or consult a registered dietitian or nutrition coach to determine your specific needs.
5.2. Adjusting Calories for Weight Goals
- Weight loss: Subtract 500-1000 calories from your daily calorie needs to create a calorie deficit.
- Weight gain: Add 250-500 calories to your daily calorie needs to create a calorie surplus.
- Weight maintenance: Consume calories equal to your daily calorie needs to maintain your weight. A nutrition coach can help you adjust your calorie intake based on your weight and health goals.
Hydration

6.1. Importance of Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for overall health, including regulating body temperature, maintaining cognitive function and supporting digestion. A nutrition coach can provide tips on staying hydrated.
6.2. How Much Water to Drink Daily
A general guideline is to drink at least 8 cups (2 litres) of water per day. However, individual needs may vary depending on factors such as age, activity level and climate. A nutrition coach can help you determine your specific hydration needs.
6.3. Hydration Tips
- Carry a reusable water bottle to remind yourself to drink regularly.
- Drink water before, during and after exercise.
- Consume water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables. A nutrition coach can suggest additional strategies for maintaining proper hydration.
Exercise and Nutrition

7.1. Exercise Types
- Beginner: Walking, swimming or gentle yoga.
- Intermediate: Running, cycling or Pilates.
- Advanced: High-intensity interval training (HIIT), strength training or power yoga.
A nutrition coach can help you choose the appropriate exercise type based on your fitness level.
7.2. Nutritional Considerations for Different Exercises
- Pre-workout: Consume a balanced snack with carbohydrates and protein 1-2 hours before exercising.
- Post-workout: Refuel with a meal or snack containing carbohydrates and protein within 1-2 hours after exercising.
- Hydration: Drink water before, during and after exercise to stay properly hydrated. A nutrition coach can provide specific nutrition recommendations based on your exercise routine.
7.3. Exercise Routines for Various Fitness Levels
- Beginner: 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity, 3-4 times per week, combined with light strength training.
- Intermediate: 45-60 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic activity, 4-5 times per week, combined with strength training.
- Advanced: 60+ minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, 5-6 times per week, combined with strength training and/or HIIT workouts. A nutrition coach can help you create a tailored exercise routine to match your fitness level and goals.
Dietary Approaches and Trends
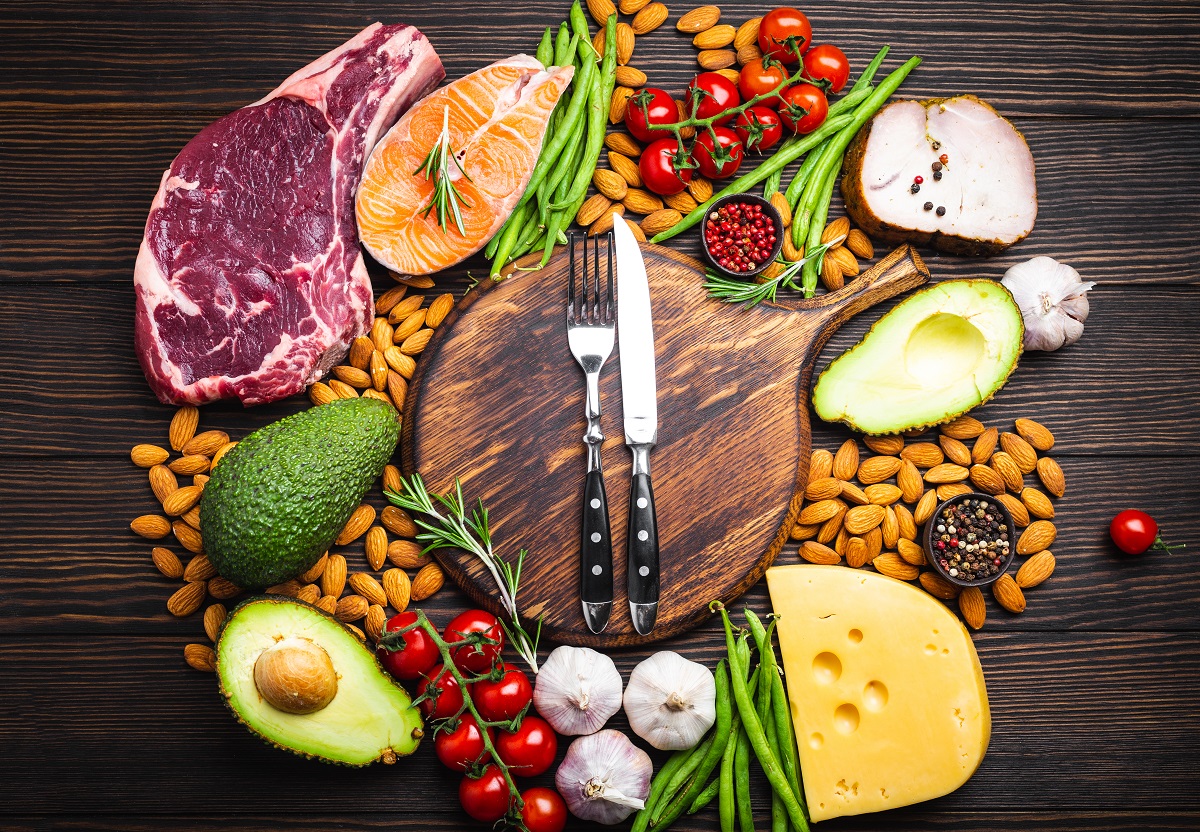

8.1. Keto
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that aims to shift the body’s primary fuel source from carbohydrates to fats. This approach can promote weight loss and improve blood sugar control in some individuals. Nutrition coaching can help you determine if the keto diet is suitable for your specific needs and guide you through the process.
8.2. Paleo
The Paleolithic (paleo) diet focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that mimic the diet of our hunter-gatherer ancestors. This includes lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, while avoiding grains, legumes, dairy and processed foods. Nutrition coaching can provide support in adopting a paleo diet while ensuring you meet your nutritional needs.
8.3. Vegan
A vegan diet eliminates all animal products, including meat, dairy and eggs. Vegans rely on plant-based sources for their nutrients, such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. Nutrition coaching is particularly helpful for vegans to ensure they receive all essential nutrients and maintain a balanced diet.
8.4. Pros and Cons of Each Approach
• Keto:
Pros include potential weight loss and improved blood sugar control. Cons include nutrient deficiencies, difficulty sustaining long-term and potential negative impacts on heart health. Nutrition coaching can help you navigate these potential challenges if you choose to follow a keto diet.
• Paleo:
Pros include the emphasis on whole foods and the elimination of processed foods. Cons include nutrient deficiencies, unsustainable for some individuals and potential negative impacts on heart health. Nutrition coaching can support you in following a paleo diet while addressing these potential concerns.
• Vegan:
Pros include potential weight loss, improved heart health and ethical/environmental benefits. Cons include potential nutrient deficiencies and the need for careful meal planning to ensure adequate nutrition. Nutrition coaching is invaluable for vegans in creating a nutritionally complete and balanced diet.
Research-backed evidence

9.1. Reliable Sources for Nutrition Information
Seek evidence-based, reliable sources when researching nutrition information. Trustworthy sources include registered dietitians, government health agencies and peer-reviewed scientific studies. A nutrition coach can help you identify credible sources of information and provide guidance based on the latest research.
9.2. Debunking Common Myths
Myth: Carbohydrates are bad for weight loss.
Fact: Consuming a balanced diet with an appropriate amount of carbohydrates can support weight loss. A nutrition coach can help you understand the role of carbohydrates in a healthy diet.
Myth: Skipping meals can help you lose weight.
Fact: Skipping meals can lead to overeating and poor nutrient intake, hindering weight loss efforts. A nutrition coach can provide guidance on meal timing and frequency for optimal weight management.
Myth: Certain foods can “burn” fat.
Fact: No specific food can directly burn fat, but a balanced diet and regular exercise can help with weight loss. A nutrition coach can help you design an effective weight loss plan that incorporates a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Conclusion for nutrition coaching guide: mastering a healthy lifestyle
Navigating the world of nutrition and wellness can be challenging, but with the right information and guidance, you can make informed choices that support your health goals. This comprehensive nutrition coaching guide has provided insights into balanced meal planning, food label interpretation, healthy dining out choices, dietary restrictions, macro and micronutrients, daily calorie needs, hydration, exercise and various dietary approaches. Remember to consult with a nutrition coach, registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalised advice and always prioritise a balanced, whole-foods-based diet, paired with regular exercise, to achieve optimal health. With the support of a nutrition coach, you can make sustainable, long-term changes that lead to a healthier lifestyle.
Here are some examples related to the various topics covered in:
“Nutrition coaching guide: mastering a healthy lifestyle”
Balanced Meal Planning Example:
A nutrition coach may help a client design a balanced weekly meal plan that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains and healthy fats. This could involve creating a shopping list, suggesting new recipes and teaching the client about proper portion sizes.
Food Label Interpretation Example:
A nutrition coach may educate a client on how to read food labels effectively, including understanding serving sizes, identifying added sugars and comparing nutrient content between similar products.
Healthy Dining Out Choices Example:
A nutrition coach might provide a client with tips and strategies for making healthier choices when dining out, such as opting for grilled or steamed dishes over fried ones, requesting sauces and dressings on the side and selecting healthier beverage options.
Dietary Restrictions Example:
A nutrition coach may work with a client who has recently been diagnosed with celiac disease, helping them identify gluten-free food options, avoid cross-contamination and ensure they still receive adequate nutrients despite the dietary restriction.
Daily Calorie Needs Example:
A nutrition coach could assist a client in calculating their daily calorie needs based on factors such as age, sex, weight, height and activity level and then provide guidance on adjusting calorie intake to support their weight goals, whether it be weight loss, weight gain or maintenance.
Hydration Example:
A nutrition coach may educate a client on the importance of proper hydration and provide practical tips for staying hydrated throughout the day, such as carrying a reusable water bottle, consuming water-rich foods and monitoring urine colour for signs of dehydration.
Exercise and Nutrition Example:
A nutrition coach may collaborate with a personal trainer to develop a comprehensive exercise and nutrition plan tailored to a client’s fitness level, goals and preferences, providing guidance on pre- and post-workout nutrition and adjusting the plan as needed to support the client’s progress.
Dietary Approaches and Trends Example:
A nutrition coach might help a client explore different dietary approaches, such as the keto, paleo or vegan diets, discussing the pros and cons of each approach and determining which one may best suit the client’s individual needs, preferences and health goals.
Research-Backed Evidence Example:
A nutrition coach can assist a client in discerning between evidence-based nutrition information and common myths, helping them make informed decisions about their diet and health. This may include debunking misconceptions about carbohydrates, skipping meals or “fat-burning” foods.
Nutrition coaching examples
By providing these examples and offering personalised guidance, a nutrition coach can help clients achieve their health and wellness goals and master a healthy lifestyle.
